Technology Decoded: Regenerative Braking
Modified On Feb 25, 2016 12:02 PM By Sahib
- 685 Views
- Write a comment
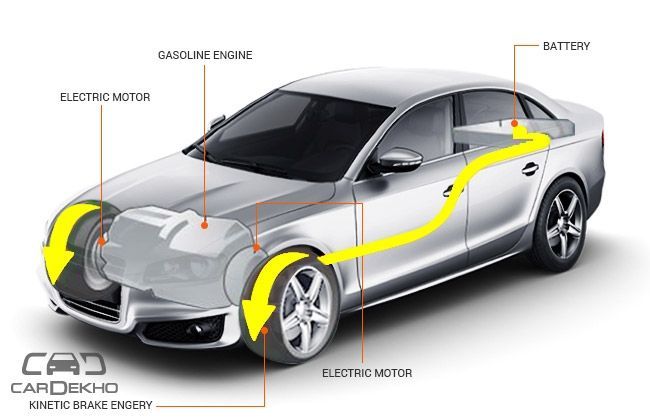
Whenever a driver applies the brakes of a vehicle, it slows down or stops and the kinetic energy gets wasted due to friction. Regenerative braking concept helps to recover as much vehicle’s kinetic energy as possible. During normal driving, if much of the braking load can be carried by regenerative braking, the friction brakes will last longer. Hybrids and all-electric vehicles are equipped with regenerative braking.
Background/Development:
- Regenerative braking was first patented by C. J. Paulson in 1908.
- In 1990, Ford manufactured Ecostar, an electric utility van with regenerative braking.
- In 1993, Toyota used regenerative braking to capitalise the stored energy in Prius hybrid car.
- Intelligent Energy Loop i.e i-ELOOP, introduced by Mazda was an innovative step forward in regenerative braking.
Technology Explained:
Regenerative braking is an advanced braking concept, in which a portion of the kinetic energy of the vehicle is stored by a storage system for further utilisation. The technology involved in regenerative braking is decoded below:
1. The components of a regenerative braking system are: Electric motors, which also act like generators (there may be individual motors at each wheel or a central motor, as shown below); High capacity battery; Electronic Control Unit (ECU).

2. When braking force is applied, rotational force of driving axle is utilised to turn the electric motors in the direction opposite to that of wheels. Hence during braking, the motor acts as a generator by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
3. This electrical energy is stored by the vehicle into a high-capacity battery and is then converted back into kinetic energy whenever the vehicle needs acceleration.

4. As the vehicle starts to accelerate, electric motor utilises the stored electric energy of the battery and operates in same direction as the direction of wheels, converting the electric energy into mechanical energy. This provides assistance to the vehicle during acceleration. The DC output of the battery is converted into AC using a DC-AC inverter.

5. ECU signals the battery through controller relay to stop sending electric energy to motors and start receiving it (through a charge controller). The motor simultaneously stops receiving electricity and starts sending current back to the battery for charging.
6. In this way, regenerative braking system plays a very important role in recovering the kinetic energy lost while braking.
Advantages of Regenerative Braking:
- Improved performance.
- Improved fuel economy.
- Reduction in brake wear.
- Emissions reduction- engine emissions reduced by engine decoupling.
Disadvantages of Regenerative Braking:
- Increased vehicle weight.
- Cars with regenerating braking systems are more expensive.
- Once the battery is fully charged, the additional charge from regenerative braking would cause voltage level of battery to rise above a safe level, which may cause severe problems.
Watch this video for better understanding of Regenerative Braking:
Also Read: Technology Decoded: Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV)










